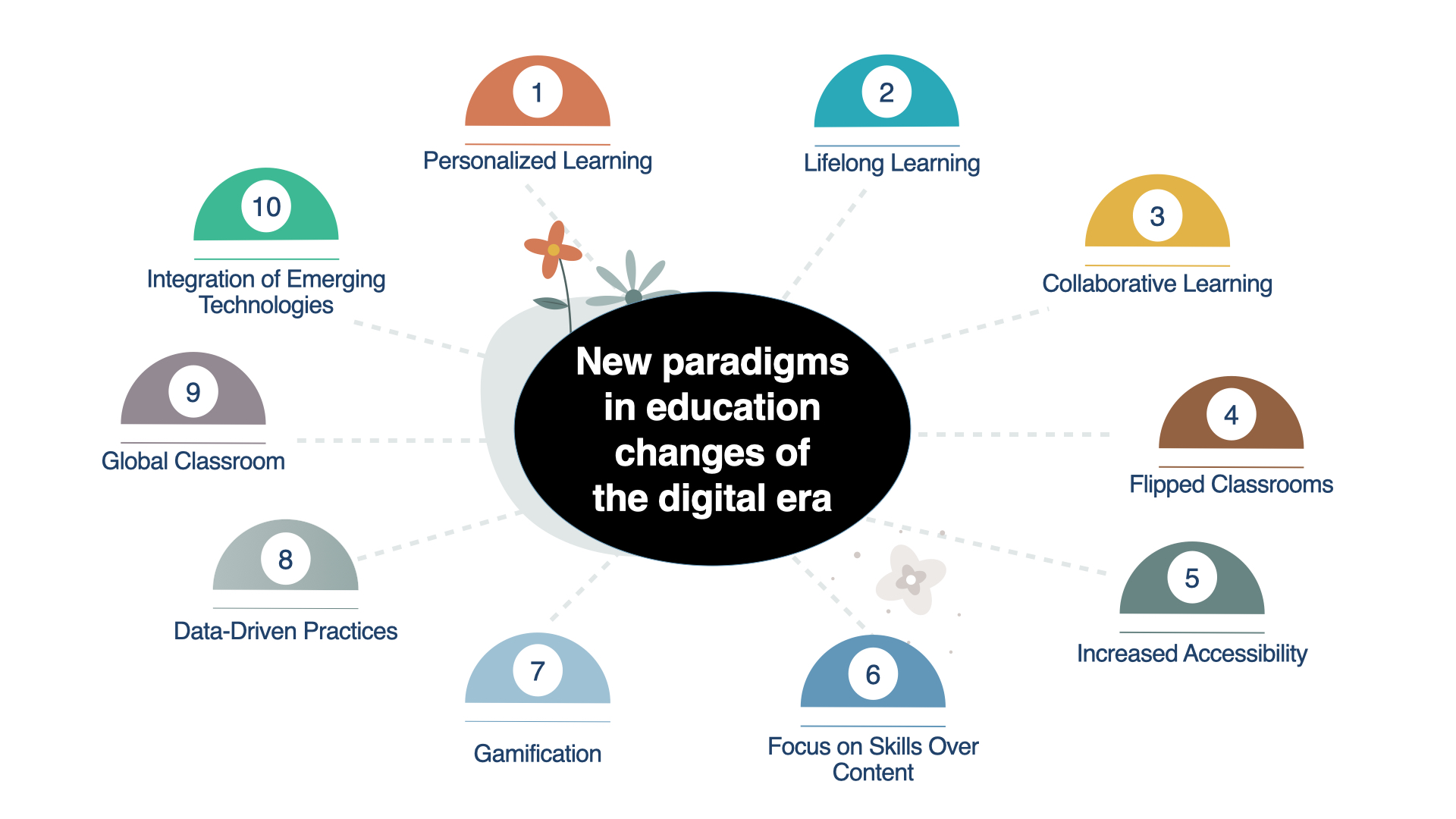
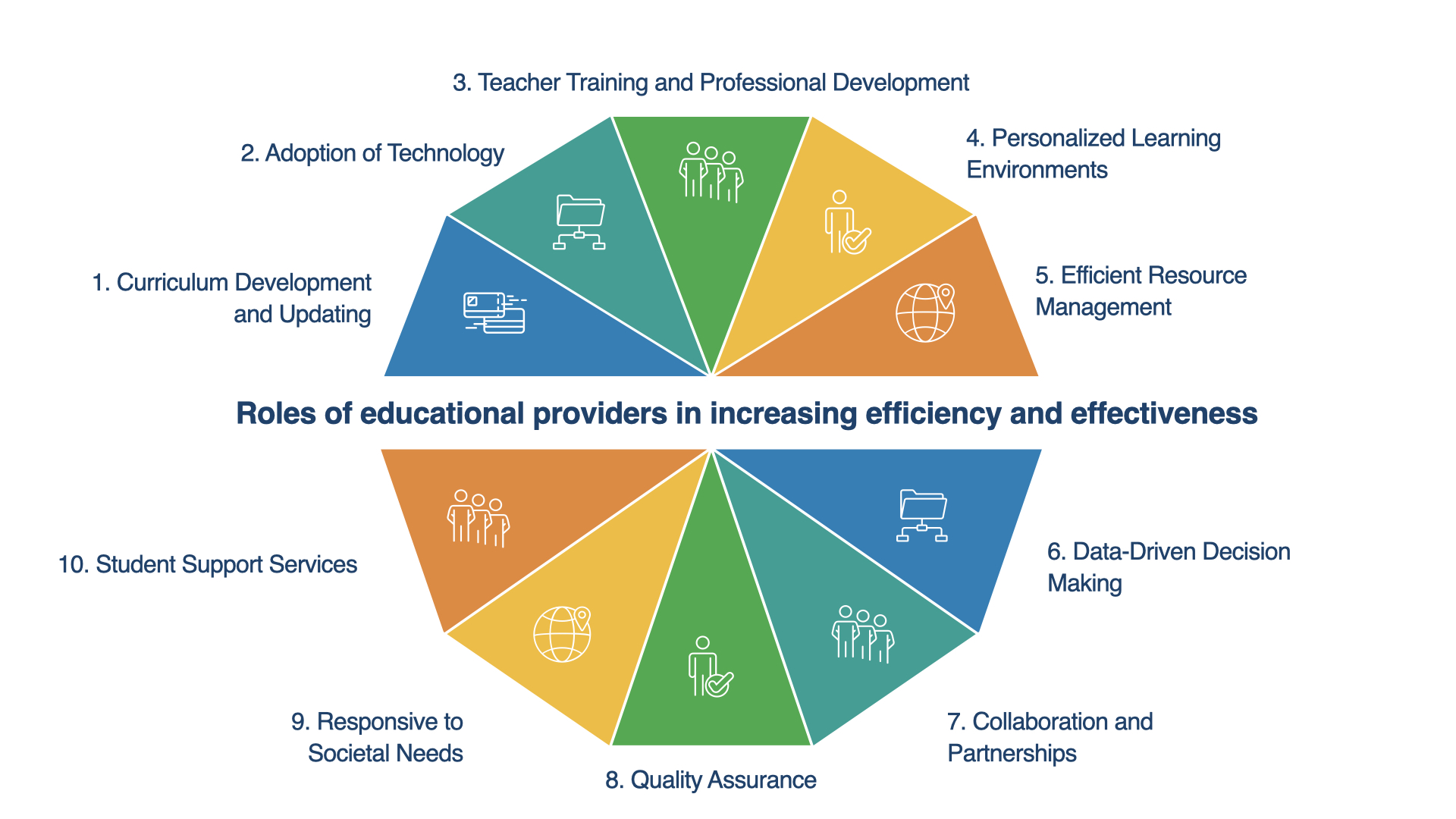
Education strategies for sustainable development (ESD) focus on integrating principles, skills, and practices related to sustainability into education at all levels. ESD aims to empower learners to make informed decisions and take responsible actions for environmental integrity, economic viability, and a just society for present and future generations while respecting cultural diversity. These strategies are vital for preparing individuals to face the challenges of today and to implement solutions for a sustainable future. Here’s an overview of key education strategies for sustainable development:

1. Curriculum Integration
Incorporating sustainability concepts across all disciplines, from science and technology to humanities and social sciences. This means not just teaching about sustainability in environmental science classes but integrating it into economics, history, art, and more to demonstrate the interconnectedness of these issues.
2. Interdisciplinary Learning
Promoting interdisciplinary approaches that involve multiple subject areas working together to address sustainability challenges. This reflects the complex, interconnected nature of the problems (like climate change), which require holistic approaches to understand and solve.
3. Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Encouraging critical thinking and problem-solving skills related to sustainability challenges. Students learn to question, analyze, and develop solutions to complex issues such as waste management, renewable energy sources, and sustainable agriculture.
4. Active Learning and Participatory Teaching Methods
Utilizing active learning and participatory teaching methods that engage students directly in learning about and working towards sustainable practices. This can include project-based learning, field trips, and community-based learning projects that allow students to engage with real-world environmental and social issues.
5. Collaboration with Local Communities
Building partnerships between educational institutions and local communities to address local sustainability issues. These collaborations can provide students with practical, real-world experiences, as well as help local communities tap into the latest academic research and technological innovations.
6. Global Perspective
Incorporating a global perspective into learning to help students understand sustainability as a global issue with local impacts. This might involve international collaborations, exchanges, or case studies on how different cultures approach sustainability.
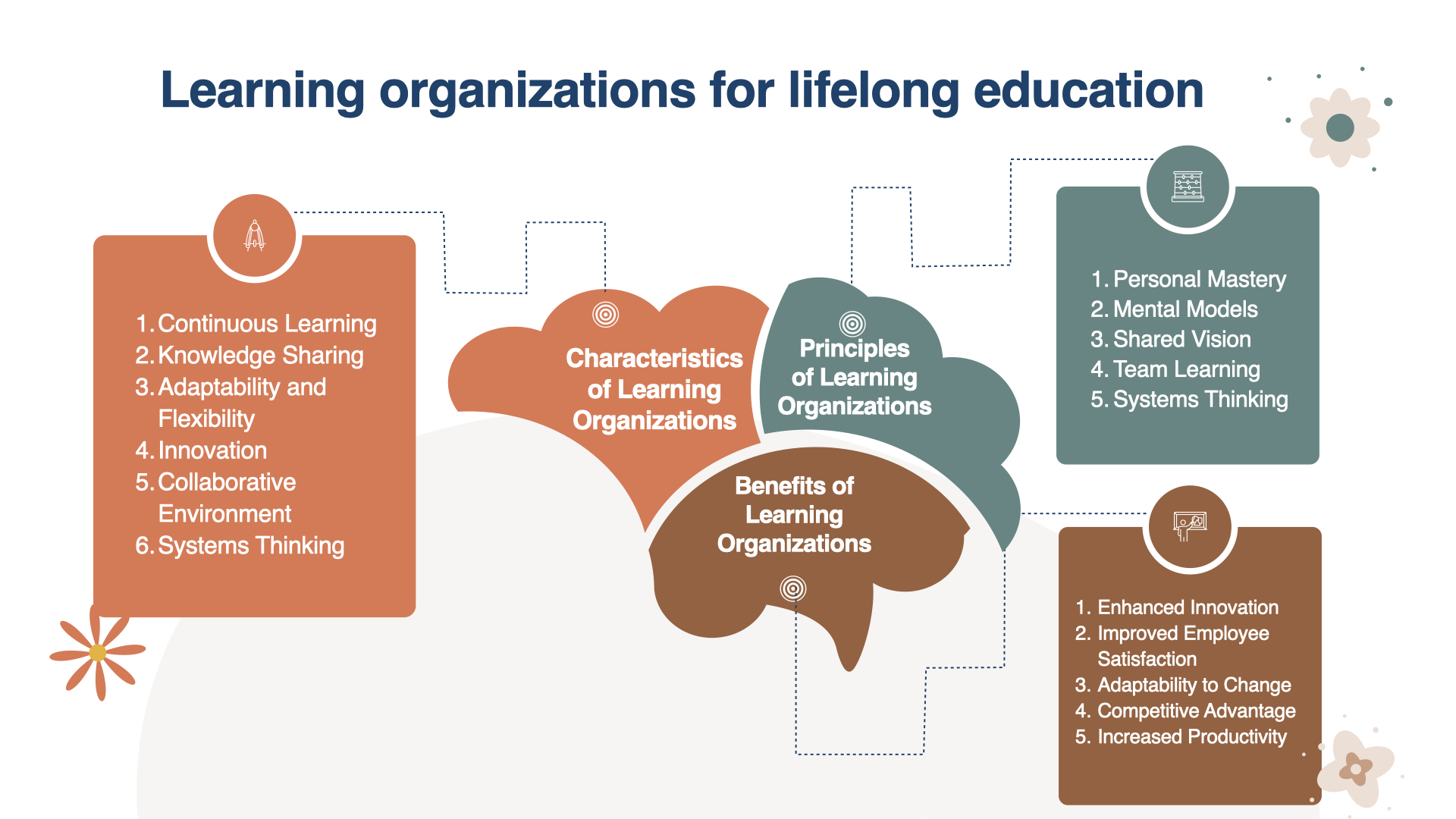
7. Sustainability Competencies
Developing specific competencies such as systems thinking, anticipatory skills, and strategic skills. These competencies help learners understand the complexities of sustainability, anticipate future scenarios, and plan and execute strategies for sustainable development.
8. Lifelong Learning
Promoting lifelong learning opportunities that allow all citizens to acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development. This includes formal education but also informal and non-formal educational pathways.
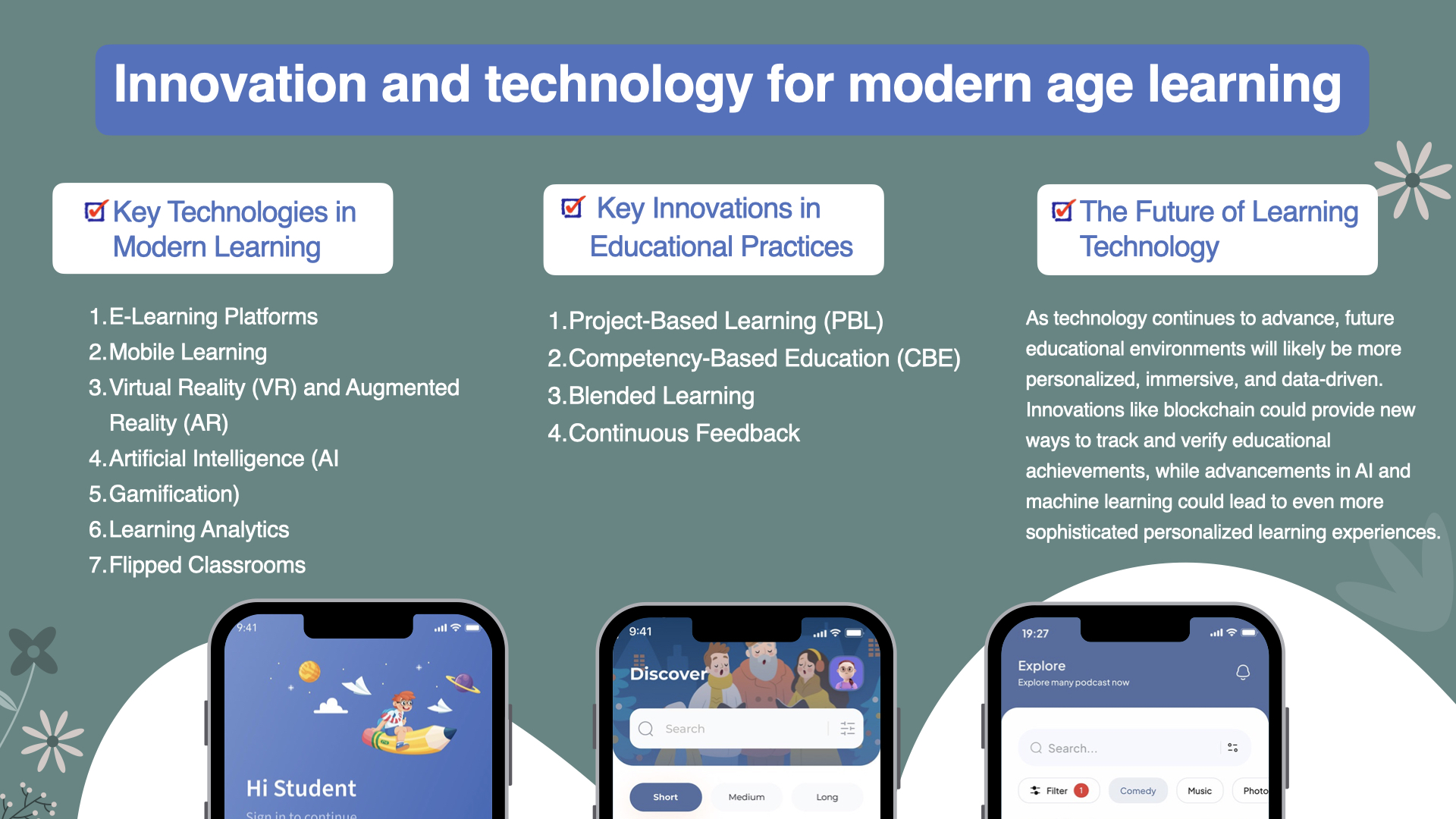
9. Technology and Innovation
Leveraging technology and innovation in education to support sustainable practices, such as using virtual reality to explore remote ecosystems or developing new tools and apps for monitoring biodiversity.
10. Assessment and Feedback
Implementing assessment strategies that reflect the principles of sustainability and provide feedback for continuous improvement. Assessments should measure not just knowledge but also attitudes, skills, and actions related to sustainability.
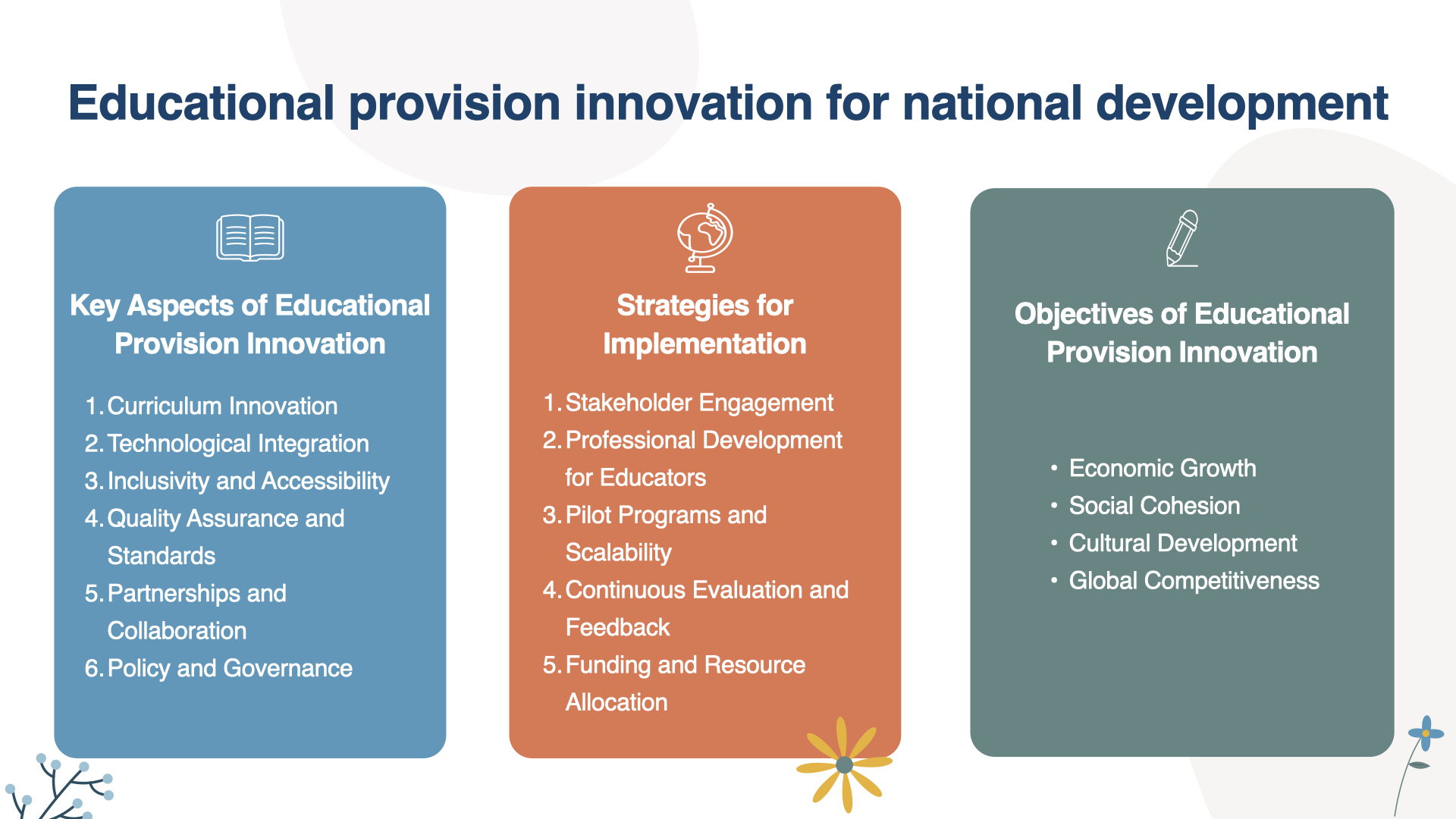
11. Educational Policy and Investment
Advocating for policies and investments that support education for sustainable development at all levels of governance. This includes securing funding for new curriculums, teacher training, and infrastructure that supports sustainable practices.
Implementing these strategies requires commitment from multiple stakeholders, including educators, policymakers, community leaders, and students themselves. Education for sustainable development is essential for creating a more sustainable future, as it equips learners with the tools to think critically and act responsibly in a rapidly changing world.